Blockchain Traceability. The financial services industry has seen blockchain, a digital distributed ledger technology, as a major game-changer. Also, blockchain’s potential uses in supply chain management have brought the technology’s traceability to the forefront. A blockchain is a decentralized ledger or digital system that securely records transactions between several parties in an immutable, verifiable, and transparent way. It may be possible to keep tabs on each step of a commercial transaction using the transaction record.
Despite the growing interest in blockchain-based traceability, many potential applications are still in the early phases of research. With the technical foundations laid out in this talk, you should be able to have a good feel for blockchain traceability. It would be helpful to provide readers with an overview of the various areas that could utilize blockchain traceability.
Blockchain and the Supply Chain Management
The majority of blockchain traceability talks center on supply chain management. One area where blockchain technology shows great promise is in supply chain management, which is in traceability. Better traceability may be possible with blockchain technology and the capacity to encode business logic through smart contracts.
Better visibility into the specifics of a product’s origin is guaranteed by blockchain technology. From its origin to its final destination, the chain of custody entails. Furthermore, the chain of custody tracking accuracy is enhanced by blockchain technology as it moves through the supply chain. Supply chain management with blockchain technology can potentially improve efficiency even in today’s technologically advanced environment. Additionally, in addition to limiting exploitative activities, blockchain technology could aid in guaranteeing auditable asset tracking.
How Can Blockchain Improve Supply Chain?
Asset tracing, transparency, and accountability could be brought about by utilizing public, private, or hybrid blockchain. When applied to logistics, blockchain technology has the potential to streamline operations, cut down on infrastructure costs, and increase productivity. In most cases, a supply chain will include a web of intermediaries, including producers, wholesalers, retailers, consumers, and auditors. The network’s participants might benefit from a streamlined process thanks to blockchain’s shared ledger technology. Shared infrastructure also has the potential to make it easier for auditors to see what all the value chain members are up to.
Because blockchain technology now includes tracking transactions, enterprise blockchain technology may revolutionize managing supply chains. Blockchain technology has three main applications in supply chain management: transparency, traceability, and traceability. By visualizing and mapping company supply chains, blockchain technology can improve operational efficiency using traceability. Another important reason to highlight the need for blockchain traceability is the ever-increasing demand for product-sourcing information. By providing customers with authentic, unchangeable, and verifiable data, blockchain technology may also aid businesses in comprehending supply chain operations.
A key component of blockchain’s traceability is the simplicity with which important data points like claims and certifications may be captured. This means it can aid in building trust, which can pave the way for open data access. After registering on the blockchain, independent attestation services check each data point for validity. The introduction of advantages for real-time updates and validation of information is what blockchain traceability is all about.
How Does Blockchain Achieve Product Traceability?
Worldwide supply networks facilitate the transfer of nearly any asset, including CPGs. Product recalls, in which specific consumer goods or raw materials are recalled to prevent disease or harm, are another issue that global supply networks handle. Litigation, dwindling sales, and the expense of replacement are just a few ways recalled consumer goods impact countless individuals throughout the globe.
A “chain of blocks” describes blockchain technology; each block represents a group of transactions. A cryptographic hash function adds each block to the existing chain of blocks. You’ll need the keys that unlock the hash function to get at the data stored in a block. The timestamp and data of the parties participating in a transaction are included in each block in a blockchain. This means it provides a thorough audit trail that can be used to track an asset’s progress through the supply chain and identify each milestone it has passed.
Implementing Blockchain Traceability
Supply chain traceability is a major application of blockchain technology. It would appear that the United States may increase its trade volume by 15% by substituting distributed ledger technology for traditional supply chain operations. Furthermore, the program can potentially increase US GDP by about 5%. With blockchain technology, it may be possible to trace the whole lifecycle of nearly any product, digital or otherwise. Blockchain traceability has the potential to facilitate the global adoption of more ethical and environmentally friendly manufacturing methods and the use of any commodity.
Finally, before the manufacturing and labeling final finished goods, many sectors rely on third-party manufacturers or multiple vendors. The white-label products are sometimes sold before they are repackaged or relabeled. Blockchain’s traceability value is all about the openness of process tracking. Manufacturers could see their value chain in action, allowing them to transport third-party products and final product labels efficiently.
Blockchain technology allows you to monitor the flow of assets, store information about them, and display their ownership records. To implement asset traceability, blockchain makes use of smart contracts. Accordingly, blockchain’s traceability could make it possible for anybody to see, in real-time, an asset’s chain of custody and its travel through the supply chain.
Real Uses of Blockchain Traceability
The practical applications of blockchain-based traceability are the most important factor to consider while grasping its consequences. One of the potential motivating elements for blockchain adoption is the capacity to offer traceability across diverse sectors. The value of traceability in the supply chain is readily apparent, as you have already observed. Improving product traceability across supply chains is something that blockchain technology can assist with. Now, we will explore the examples of how traceability is used in different areas.
Supply Chain
The decentralized nature of blockchain makes its supply chain tracing applications very obvious. Distributed ledger technology (blockchain) applications in the supply chain have the potential to enable worldwide trading partners to conduct safe transactions and reach consensus on shared facts, which would improve efficiency, transparency, and visibility. The immutability of items’ origin is the main use case for blockchain in the supply chain. In addition, supply chain use cases that employ blockchain-based traceability also provide respite from the hassles of reconciliation with different partners. The most significant benefit blockchain technology may provide is the ability to conduct track and trace analyses in real-time.
Agriculture
Several problems plaguing the agricultural industry can be efficiently addressed using blockchain technology’s traceability features. The use of traceability in agriculture has the potential to enhance crop production efficiency and better manage agricultural financing. Blockchain and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors could improve agricultural field monitoring, for instance, when used together. Data acquired for several crop field factors, including soil moisture, temperature, light, humidity, and pH, might be better documented using blockchain technology. Further, farmers may be able to make better agricultural decisions using machine learning algorithms and predictive models. In addition, the management of agricultural finance can benefit from blockchain traceability. All parties involved in the food production process, including farmers, can share data, and auditors can do their jobs well.
Fashion
Counterfeit goods are a major revenue drain for the fashion sector every year. The market’s trust in fashion labels is also dwindling. Thus, blockchain technology has the potential to aid in tracking the supply chain of products, which might lead to a more trustworthy basis for consumers. Customers can learn about the origins of fashion products with the help of blockchain technology. Another potential advantage of traceability is the use of unique identifiers to confirm the authenticity of products. With the help of unique identification, you can track the product’s progress along the value chain.
Food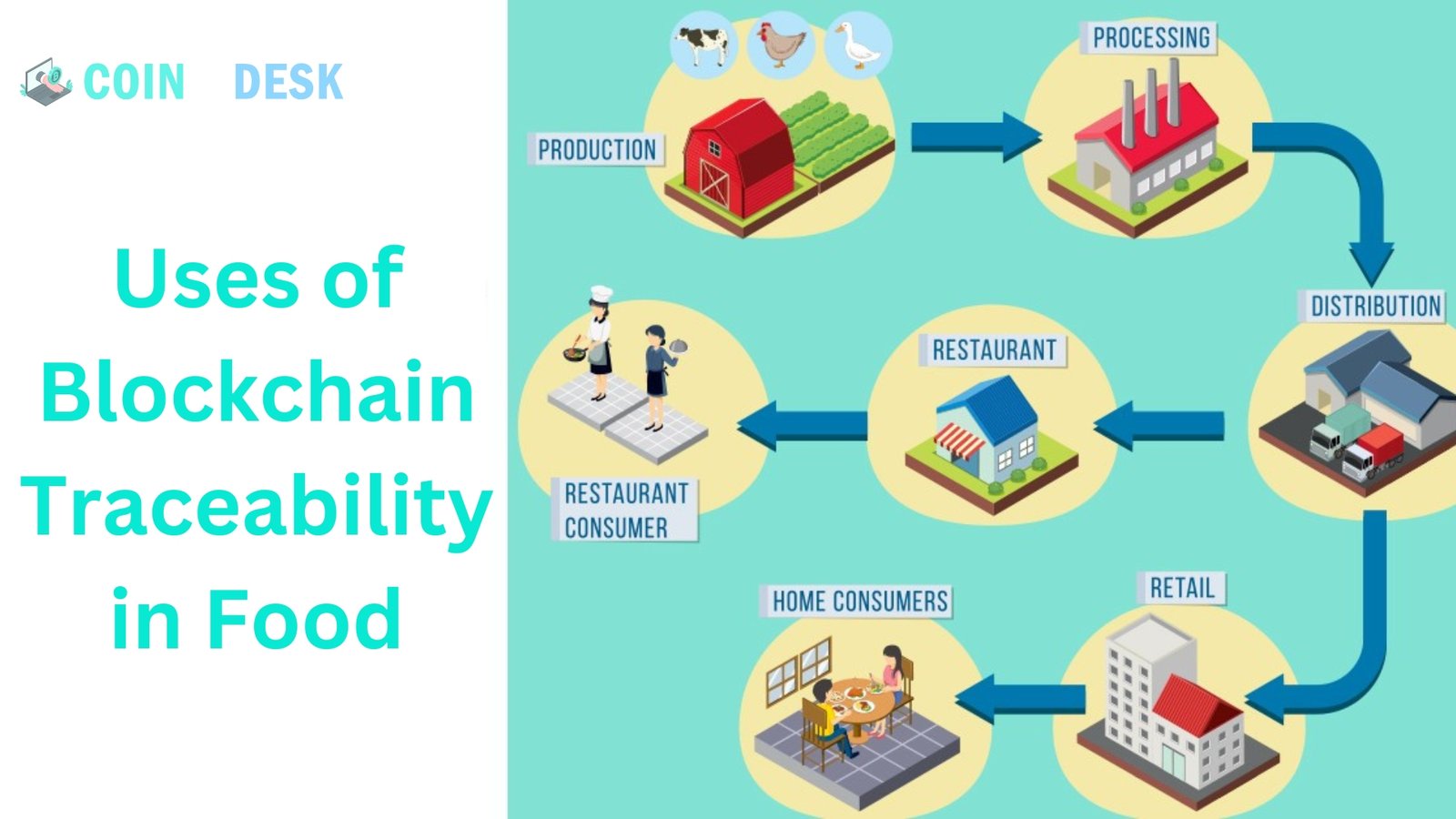
The quality standards people expect from the food they buy always change. Consumers are more curious about the origins and production methods of the food they buy. Consumers may be able to learn more about the provenance of their food if it is traceable using blockchain technology. On top of that, it lets you see details about the food’s origins and how fresh it is. Each link in the food supply chain is responsible for entering product details into the database. Consequently, there may be clear benefits to food supply chain traceability, such as decreased food fraud and misleading labeling.
Manufacturing
Blockchain technology could simplify and secure data exchange for manufacturing companies operating in complex supply networks. The industrial sector might benefit from blockchain technology’s traceability by accessing an immutable digital ledger of all goods, components, and raw materials. Therefore, it can guarantee rapid expansion of end-to-end production process visibility. Meanwhile, a centralized point of trust could be accessed by everyone involved in the production process. Most importantly, blockchain technology has the potential to assist manufacturers in increasing the traceability of their supply chains. Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain technology, for instance, could facilitate product data collection at various stages of the supply chain, including but not limited to temperature, pH, moisture, and other characteristics.
Conclusion
One of the most striking aspects of blockchain technology is its ability to be traced back to its fundamental design element. The immutable, secure, and verifiable record-keeping of transactions on the blockchain lays the groundwork for tracing. By providing a comprehensive audit record of network transactions, blockchain technology can significantly contribute to enhanced traceability.
Furthermore, blockchain traceability shows promise due to its security and interoperability features. Aside from the numerous potential applications in various industries, blockchain traceability also has the power to bring about next-generation traceability.


